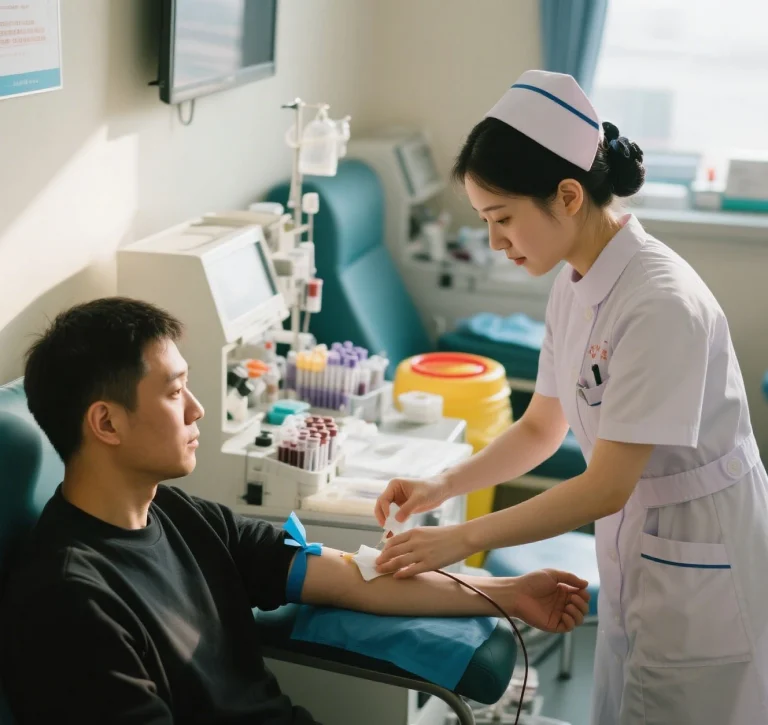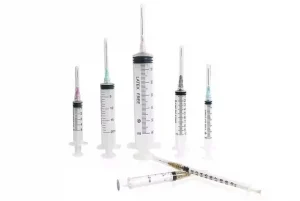
Key Components of a Hypodermic Needle Syringe
The Barrel: Structure and Material Considerations
The barrel of the hypodermic needle syringe is an important part that is created for having and measuring the liquid medication accurately. Its cylindrical shape enables accurate adjustment when you need to extract or inject fluid. The shape is generally tubular, thus providing accurate regulation of the fluid one is drawing or injecting.
Material Types and Their Benefits
Barrels tend to be plastic or glass. Plastic barrels are typically made from polypropylene, so they are durable and inexpensive. This makes them light and unbreakable, which is excellent for single-use applications. However, having glass barrels ensures very good chemical resistance and clarity, necessary for medications that may become damaged by interaction with plastic.
Design Features for Precision and Safety
Precise-engineered barrel to ensure accurate dosing. There are graduated markings along the barrel to ensure the right measurement. There’s also a barrel end with flanges that help you hold the tolerances better, so some of it won’t slip out.
The Plunger: Mechanism and Functionality
The plunger is responsible for drawing in and expelling fluids from the syringe. Its movement within the barrel must be smooth to maintain control over fluid flow.
Ergonomic Design for Ease of Use
The design of the plungers was equally ergonomic, which was to increase comfort as well as cause the laundry effect since the design was on par with a plunger. Finally, a thumb rest at the distal tip of the plunger allows for easy movement with little activation, and this is crucial in longer procedures. At the end of the plunger is a thumb rest to ensure easy manipulation without much effort, an important feature during long procedures.
Seal Integrity and Fluid Control
You seal between the plunger and barrel is also critical for no leaks. The plunger also has a soft rubber tip which creates an airtight seal so that you can’t just suck a lot of whatever specific fluid you’re using back up into the syringe. This seal has to be strong enough to endure all sorts of pressures without sacrificing functioning. It needs to be strong enough to stand up to all sorts of imposed pressures while still working as intended.
The Needle: Critical Attributes and Variations
The needle is a pivotal component that directly interacts with patient tissues, making its design critical for effective medication delivery.
Gauge Sizes and Their Clinical Implications
The gauge of a needle indicates the diameter; a smaller gauge needle has a larger diameter. Patient comfort and medication flow rate are impacted by the choice of gauge. For example, heavier medications need larger gauges for a smoother administration, however, smaller gauges limit the pain during the administration. Thicker medication needs a larger gauge to help it flow, but a smaller gauge to reduce the pain during injection, for example.
Needle Lengths for Different Applications
Depending on their purpose, needles are available in different lengths. Subcutaneous injections require a short needle to inject medication into the fatty tissue just beneath the skin. Deeper penetration into muscle tissue means longer needles are used for intramuscular injection. Intramuscular injections require deeper penetration into the muscle tissue, therefore longer needles are used for injection.
Functional Aspects of Hypodermic Needle Syringes
Mechanism of Action in Medication Delivery
Knowing how different injection types work is key to proper medication administration pharmacokinetics. The purpose of IM (intramuscular) injections is to put the drug into muscle tissue, and since this tissue has a rich vascular supply, the fastest absorption occurs. Meanwhile, subcutaneous injections instill drugs into fatty tissue below the skin with a slower absorption rate but higher patient comfort.
Which methods are used may vary according to the type of drug administered and how quickly an effect is desired, suggesting that proper method selection can be an important part of the management of certain clinical situations. As different techniques can be employed based on medication and concentration of drug for absorption, the translated value of techniques should be taken wisely for clinical circumstances as per requirement.
Safety Features in Modern Designs
Modern hypodermic needle syringes incorporate safety features aimed at protecting healthcare professionals from needlestick injuries while ensuring patient safety during administration.
Retractable Needles and Safety Caps
Needles that retract back into the syringe after use greatly reduce the risk of exposure to contaminated sharps. Safety caps are used to add another level of safety as they cover needles after use until disposal. Safety caps, which cover needles after injection and remain on the needle until disposal, provide an additional level of protection.
Innovations to Reduce Needlestick Injuries
Needleless systems or blunt-tip cannulas are innovative designs against needlesticks whereby sharp tip is completely avoided during specific procedural or sampling processes.
Future Trends in Hypodermic Needle Syringe Technology
Advances in Material Science
The evolution of hypodermic needle syringe technology is significantly influenced by advances in material science. These developments are crucial for enhancing safety, sustainability, and functionality.
Biocompatible Materials for Enhanced Safety
Biocompatible materials are being utilized more to increase the safety of hypodermic needle syringes. These materials help reduce adverse reactions in the body that come in close contact with human tissues, making it allergy-free and having low chances of infections. Recent advances in polymer science have yielded new materials with an even greater compatibility with body tissue to enable safer and more effective delivery of therapeutic agents.
Eco-Friendly Alternatives for Sustainability
The rising health consciousness among the masses is leading to the development of eco-friendly materials for syringe production due to escalating environmental concerns. There are alternative materials with lower environmental impact, such as biodegradable plastics or materials that biodegrade more rapidly than traditional plastics, that currently have certain manufacturers like Medco investigating alternatives. They not only reduce medical waste but also comply with the sustainability goals of the world, which is why they are the first choice of all those healthcare service providers having innovative approaches.
Medco’s Role in the Evolution of Medical Devices
Medco’s Contributions to Hypodermic Needle Technology
Medco has steeped itself in innovation and quality in hypodermic needle technology for years and continues to advance the technology. In order to produce syringes that fulfill the changing requirements of healthcare practitioners and patients, the organization is heavily investing in research and development for safer more economical syringes. Medco is striving to include advanced materials and smart technology in their products, signifying a step forward in high standards of medical devices worldwide.
Exploration of Medco’s Broader Product Range
Medco additionally manufactures a full line of medical devices in the patient room and other settings, in addition to hypodermic needles. They are globally recognized for their comprehensive range of advanced infusion systems,
medical devices
, and surgical instruments, showcasing their profound expertise in cutting-edge medical technology. This ensures that funders, physicians, and patients have a continuous stream of new alternatives so that they can adapt to changing industry dynamics while providing the best possible care, which Medco cultivates by steadily growing its product array.